- Abigail Hynes Murphy Fashion Film Installation Lighting Design Music abigail-hynes-murphy
- Adam Doyle 3D Character Design Digital Design Environment Game Design Lighting Design Motion Graphics Sculpture adam-doyle
- Ailill Martin Film ailill-martin
- Áine Osborne Painting aine-osborne
- Aisha Bolaji Film Television aisha-bolaji
- Aisling Deegan Cultural Future Technologies Psychology Radio Research Science User Experience aisling-deegan
- Alan Bright Music Psychology alan-bright
- Alan O Connor Education Music Psychology Research alan-o-connor
- Alex Madigan Vaughan alex-madigan-vaughan
- Alexandra Ciolan 3D Character Design Design Thinking Exhibition Design Psychology Sculpture alexandra-ciolan
- Alexandra Furey Advertising App Cultural Design for Change Education Motion Graphics User Experience alexandra-furey
- Amber Johnson Education Environment Psychology Research amber-johnson
- AmberAmelia Kelly Drawing Film Illustration amber-kelly
- Amy Caulfield App Branding Cultural Digital Design Motion Graphics Performance User Experience amy-caulfield
- Amy Gannon 3D Character Design Cultural Digital Design Drawing Exhibition Design Film Illustration Painting Set Design Television amy-gannon
- Amy Rintoul App Business amy-rintoul
- Andy Sherlow Film andrew-sherlow
- Anita Horvath Psychology anita-horvath
- Anna Brick Advertising Book Design for Change anna-brick
- Annie Condon Psychology annie-condon
- Annie Fox 3D Character Design Exhibition Design Film Product Design Set Design annie-fox
- Anuoluwa Kuye Character Design anuoluwa-kuye
- Aoibhe Rice 3D Architecture Crime Design Thinking Digital Design Drawing Film History Performance Research Set Design Space Exploration Television aoibhe-rice
- Aoife Carroll Book Cultural Design for Change Illustration aoife-carroll
- Aoife Dowd Bedidi 3D Future Technologies Music Research aoife-dowd-bedidi
- Aoife Haden Film aoife-haden
- Aoife Kerrigan (Ní Chiaragáin) 3D Architecture Character Design Exhibition Design Sculpture Set Design Space Exploration aoife-kerrigan
- Aoife-Joy Fitzmaurice 3D Digital Design Drawing Film Illustration Painting Performance Set Design Television aoife-joy-fitzmaurice
- Ashling Smith App Charity Design Thinking Digital Design ashling-smith
- Ava Russell Character Design ava-russell
- Ava Shepherd AI App Cultural Design for Change Design Thinking Digital Design Education Ethics User Experience Website ava-shepherd
- Beck Garrigan Advertising Branding Charity Design for Change Digital Design Education Ethics Healthcare Illustration Social Justice User Experience beck-garrigan
- Becky Corrigan Accessibility App Digital Design Future Technologies Game Design Music Research User Experience Website becky-corrigan
- Ben Condell ben-condell
- Ben Hackett Character Design Fashion Film Performance Set Design Television ben-hackett
- Beth McLoughlin Design for Change Environment Installation Music beth-mc-loughlin
- Bethany Renwick Cultural Equality Fashion Life Sciences Psychology Research Science Social Justice bethany-renwick
- Brandon O Sullivan 3D Architecture Design for Change Design Thinking Digital Design Education Engineering Entrepreneurship Environment Exhibition Design Film Future Technologies Game Design Product Design Research Science Set Design brandon-o-sullivan
- Caitlin Nickels Film caitlin-nickels
- Caitriona Brennan Design Thinking Exhibition Design Motion Graphics Product Design User Experience caitriona-brennan
- Caitríona McGuinness Character Design Digital Design Drawing Film Illustration Motion Graphics caitriona-mc-guinness
- Campbell Gibson Film campbell-gibson
- Caoimhe Gallagher Lawson Film caoimhe-gallagher-lawson
- Carl Lovett Film Performance carl-lovett
- Carmel Mueller Psychology carmel-mueller
- Caroline Kirwan Psychology caroline-kirwan
- Caroline Mackey 3D Character Design Film caroline-mackey
- Cassie-Lee O'Rourke Drawing Painting cassie-lee-o-rourke
- Céin O'Dowd Engineering Entrepreneurship Music Product Design User Experience cein-o-dowd
- Celt Stephenson Li Sports + Fitness User Experience celt-stephenson
- Charlotte Parker Accessibility Diversity Future Technologies Psychology Research charlotte-parker
- Chloe Bevan chloe-bevan
- Chlöe Fitzgerald Music Performance chloe-fitzgerald
- Chloe O Connor Psychology chloe-o-connor
- Chris McConnon Espinola Character Design Digital Design Drawing Film Illustration Lighting Design chris-mc-connon-espinola
- Cian Bolger Digital Design cian-bolger
- Cian Handschuh Architecture Cultural Energy Environment Installation Painting Property Sculpture Wildlife cian-handschuh
- Cian Ryan 3D History cian-ryan
- Ciara Adamson Branding Engineering Management Music Performance Radio ciara-adamson
- Ciara Davis Accessibility App Branding Cultural Design for Change Design Thinking Illustration Motion Graphics Music Performance User Experience ciara-davis
- Ciara Drinan Set Design ciara-drinan
- Ciara Farrell Character Design Drawing Film Illustration Set Design ciara-farrell
- Ciara Hogan Character Design Fashion Film ciara-hogan
- Ciara Kelly Digital Design Drawing Film Product Design Set Design ciara-kelly
- Ciaran Byrne Psychology ciaran-byrne
- Cillian Brennan Covid-19 Film Music Television cillian-brennan
- Clemente Gonzales AI Future Technologies Research User Experience Website clemente-gonzales
- Clodagh Byrne Cultural Film Radio Television clodagh-byrne
- Clodagh McCarthy clodagh-mc-carthy
- Conor Waldron Film Television conor-waldron
- Conor Weldon Accessibility AI Business Data Visualisation Education Engineering Entrepreneurship Future Technologies Healthcare Installation Psychology Research User Experience conor-weldon
- Cormac Rice Diversity Education Engineering Life Sciences Science cormac-rice
- Courtney Mulligan Character Design courtney-mulligan
- Daire Lynch Psychology Sports + Fitness daire-lynch
- Damien Tallon 3D Architecture Character Design Drawing Environment Film Game Design Illustration Lighting Design Motion Graphics Painting Set Design Television damien-tallon
- Dan Sony Psychology Research dan-sony
- Dan Kavanagh Music Research daniel-kavanagh
- Darren O'Malley Psychology darren-o-malley
- David Carvill 3D Installation Sculpture david-carvill
- Dean Connolly Digital Design Exhibition Design Motion Graphics Music Psychology Research dean-connolly
- Derek Reid App Website derek-reid
- Eamonn Cooke Business Ethics Game Design Psychology Research eamonn-cooke
- Eamonn Mac Mahon Film eamonn-mac-mahon
- Eimear Branigan Psychology eimear-branigan
- Eleanor Keane Psychology eleanor-keane
- Elise Mc Elroy 3D Character Design elise-mc-elroy
- Lil Jones Business Cultural Digital Design Diversity Entrepreneurship Exhibition Design Management Music Performance Radio elizabeth-jones
- Ellen Doherty Drawing Film Illustration ellen-doherty
- Ellen Mc Hugh Set Design ellen-mc-hugh
- Ellen Wise Film Performance ellen-wise
- Ellie McDonald Education Psychology ellie-mc-donald
- Ellie Mulligan 3D Book Character Design Cultural Design for Change Design Thinking Digital Design Drawing Ethics Fashion Film Painting Set Design Television ellie-mulligan
- Elsa Murray 3D Architecture Design Thinking Digital Design Exhibition Design Film Lighting Design Performance Research Set Design elsa-murray
- Emer O' Byrne Fashion Psychology emer-o-byrne
- Emilia Rigaud Cultural Diversity Energy Environment Equality Ethics Exhibition Design Fashion Film Installation Music Print Making Research Sculpture Set Design Social Justice Space Exploration Website emilia-rigaud
- Emily Deveney emily-deveney
- Emily Lannin Branding Design for Change Design Thinking Digital Design Environment Future Technologies Government Motion Graphics Research User Experience Website emily-lannin
- Emily Sheridan Psychology emily-sheridan
- Emily Toma Design Thinking Digital Design User Experience emily-toma
- Emily-Jane Good Plunkett Psychology emily-jane-good-plunkett
- Emma Murphy App Design for Change Design Thinking Digital Design Education Healthcare User Experience emma-murphy
- Emma Nalty Painting emma-nalty
- Emma Nolan Design for Change Design Thinking Digital Design Entrepreneurship Motion Graphics Research User Experience emma-nolan
- Emma Raftery emma-raftery
- Emma Yuan Cultural Design for Change Energy Environment Exhibition Design History Life Sciences Lighting Design Product Design Set Design Website Wildlife emma-yuan
- Eoghan Fitzmaurice Music eoghan-fitzmaurice
- Eoin O Faherty Data Visualisation Music eoin-o-faherty
- Erin Doyle Psychology erin-doyle
- Eva Kenna Cultural eva-kenna
- Fay-Orion Antar fay-orion-antar
- Fíadh Flood Crime Psychology Research Science Television fia-flood
- Filip Slanina Film Lighting Design filip-slanina
- Finn Mc Keon Character Design Design Thinking Drawing Illustration Motion Graphics finn-mc-keon
- Fionn Beardon Film fionn-beardon
- Fionn O Lochlainn Branding Data Visualisation Design Thinking Digital Design Entrepreneurship Future Technologies Motion Graphics Research User Experience Website fionn-o-lochlainn
- Freya Meldrum Character Design Design Thinking Film Performance freya-meldrum
- Galena Murray Film galena-murray
- Gemma Coleman gemma-coleman
- Jill Clinch Sculpture gillian-clinch
- Grace Brennan Accessibility Advertising Charity Design for Change Design Thinking Digital Design Environment Ethics Exhibition Design Installation Motion Graphics Social Justice User Experience Website grace-brennan
- Gregory O'Reilly gregory-o-reilly
- Greta Mikulskaja 3D Character Design Sculpture greta-mikulskaja
- Hannah Kelly Family Film hannah-kelly
- Hannah Khan Set Design hannah-khan
- Hannah Moran App Branding Design for Change Design Thinking Digital Design Motion Graphics User Experience hannah-moran
- Hannah Murphy hannah-murphy
- Heather Brennan heather-brennan
- Heather Kearns 3D Character Design Digital Design Game Design heather-kearns
- Hetty Lawlor Accessibility Architecture Book Business Character Design Charity Crime Cultural Design for Change Diversity Drawing Education Energy Environment Equality Ethics Exhibition Design Family Fashion Government Healthcare History Illustration Life Sciences Lighting Design Painting Politics Print Making Property Protest Psychology Research Science Sculpture Social Justice Transport + Travel Wildlife heather-lawlor
- Holly Greene holly-greene
- Holly Langan Film holly-langan
- Holly O'Sullivan Covid-19 Crime History Performance Research holly-o-sullivan
- Ian Fallon Diversity Equality Film ian-fallon
- Ieva Valentinaviciute Psychology ieva-valentinaviciute
- Isabel Goodall isabel-goodall
- Isabella Redmond Advertising App Branding Data Visualisation Design Thinking Education Healthcare Motion Graphics Research User Experience isabella-redmond
- Isaré Sánchez Gómez 3D Architecture Cultural Drawing Exhibition Design Fashion Film Performance Set Design Television isare-sanchez-gomez
- Jack Dwyer jack-dwyer
- Jack Leach Film Television jack-leach
- Jack Wells Education Ethics Psychology Research Science jack-wells
- Jack Whittle jack-whittle
- Jade Kelly User Experience Website jade-kelly
- Jake Black AI App Engineering Website Wildlife jake-black
- Jake Hoffman jake-hoffman
- Jen Gallagher jennifer-gallagher
- Jennifer Whitney Rothwell jennifer-whitney-rothwell
- Jessica Bradshaw Character Design jessica-bradshaw
- Joe Phelan AI Cultural Design for Change Design Thinking Digital Design History Motion Graphics Print Making joe-phelan
- Joe Crossen 3D App Branding Design for Change Design Thinking Digital Design Environment Ethics Future Technologies Motion Graphics Product Design Social Justice User Experience joseph-crossen
- Joseph O'Brien Film Psychology Research Science joseph-o-brien
- Joey O'Gorman (Joseph O'Gorman) Music Research joseph-o-gorman
- Joshua Corcoran Psychology joshua-corcoran
- Joshua Niall Murphy Illustration Painting Print Making joshua-murphy
- Julia George julia-o-doherty
- Juliette Kilcoyne App Branding Cultural Design for Change Diversity Environment Future Technologies Government Motion Graphics User Experience juliette-kilcoyne
- Kamile Vaitkeviciute Installation kamile-vaitkeviciute
- Karen Reilly Branding Cultural Environment Film Television karen-reilly
- Karla Byrne karla-byrne
- Katarzyna Haśnik Accessibility Cultural Data Visualisation Design for Change Design Thinking Digital Design Education Ethics Future Technologies Healthcare Product Design Psychology Research User Experience katarzyna-hasnik
- Kate Connolly Psychology kate-connolly
- Katelyn Ansbro 3D Character Design Environment Exhibition Design Film Installation Painting Sculpture Set Design Wildlife katelyn-ansbro
- Katelyn Markham O'Halloran Film Music Set Design Television katelyn-markham-o-halloran
- Katerina Hruba Cultural Education Environment Life Sciences Psychology Research Science Wildlife katerina-hruba
- Katie Brett Set Design katie-brett
- Katie Callan Character Design Drawing Film Illustration katie-callan
- Katie Carvill Character Design Sculpture katie-carvill
- Katie O Hara Character Design Illustration Painting katie-o-hara
- Kellie Doherty Digital Design Drawing Film Illustration Motion Graphics Television Website kellie-doherty
- Kelly Lane Film Television kelly-lane
- Klaudia Sidwinska Education Psychology Research Science klaudia-sidwinska
- Laoise Doyle laoise-doyle
- Laoise Rowe Music Psychology Research laoise-rowe
- Lauren Battersby Advertising App Digital Design Product Design Property Psychology Research User Experience lauren-battersby
- Lauren Doherty 3D Film Television lauren-doherty
- Lauren Harkin Advertising App Branding Character Design Covid-19 Design for Change Digital Design Family Healthcare Illustration Motion Graphics User Experience lauren-harkin
- Lauren Mc Govern Book Protest lauren-mc-govern
- Leah Merriman Character Design Design Thinking Digital Design Drawing Environment Film Painting Psychology Television Website leah-merriman
- Lee Hersee 3D Architecture Design for Change Digital Design Future Technologies Game Design lee-hersee
- Liam Prenter Morris liam-prenter-morris
- Lily O' Neill Drawing Film Illustration Performance Set Design Television lily-o-neill
- Linsey Corcoran Psychology Sports + Fitness linsey-corcoran
- Lisa Folschette Film lisa-folschette
- Lochlann Megannety AI Book Branding Design for Change Design Thinking Exhibition Design Future Technologies Motion Graphics User Experience lochlann-megannety
- Lorna Corcoran Psychology lorna-corcoran
- Luca Tinley Music luca-tinley
- Lucía Dwyer Film lucia-dwyer
- Lucy Maher Character Design Fashion Film lucy-maher
- Luke O'Shaughnessy Film luke-o-shaughnessy
- Mai Maher Architecture Design Thinking Digital Design Film Set Design Television mai-maher
- Mara Matagne 3D Character Design Cultural Design Thinking Diversity Equality Exhibition Design Installation Lighting Design Music Performance Product Design Protest Psychology Sculpture Social Justice mara-matagne
- Marcus Fitzsimons AI Digital Design Future Technologies Research Website marcus-fitzsimons
- Maria Malone maria-malone
- Mari Naughton Diversity Film mariana-naughton
- Mateusz Luczaj 3D Character Design Digital Design Film Property Sculpture Set Design Space Exploration mateusz-luczaj
- Matt Rankin 3D Film matthew-rankin
- Matthew Ryan matthew-ryan
- Mattie Hogan 3D Engineering Installation Product Design mattie-hogan
- Maya Browne Branding Design for Change Motion Graphics Website maya-browne
- Megan Coleman App Branding Cultural Design Thinking Digital Design Installation Motion Graphics Product Design User Experience megan-coleman
- Megan Colville Book Character Design Design for Change Design Thinking Digital Design Education Illustration Print Making megan-colville
- Megan Culleton Character Design Design Thinking Drawing Fashion Film Performance Television megan-culleton
- Megan Johnston Music Psychology megan-johnston
- Megan Wynne megan-wynne
- Meghan O'Shaughnessy Film meghan-o-shaughnessy
- Melissa Murphy Life Sciences Psychology melissa-murphy
- Mella Carron Business Covid-19 Cultural Design Thinking Education Entrepreneurship Family Film Government Healthcare History Music Painting Performance Radio Research Social Justice mella-carron
- Mhairi O Connell Environment Ethics Fashion Psychology mhairi-o-connell
- Mia Yip-Breen Set Design mia-yip-breen
- Micah Encarnacion Engineering Film Music Performance micah-encarnacion
- Michelle Bardon Character Design Film Illustration michelle-bardon
- Naoe Ebeniel Timbang 3D Character Design Drawing Film Illustration naoe-timbang
- Naoise Kettle Film naoise-kettle
- Natalia Nowak Psychology natalia-nowak
- Niall Smith Energy Healthcare Psychology niall-smith
- Níamh Herkommer Character Design Film niamh-herkommer
- Niamh Hughes User Experience niamh-hughes
- Nick Willoughby nick-willoughby
- Oisin Donnelly Drawing Illustration Painting Print Making oisin-donnelly
- Oisín Heffernan oisin-heffernan
- Oisin Keegan oisin-keegan
- Oliver Mendoza 3D Character Design Digital Design Sculpture oliver-mendoza
- Olivia Wynne Psychology Sports + Fitness olivia-wynne
- Olwen Yappa 3D Character Design Lighting Design Performance Set Design olwen-yappa
- Patrick Barnes Installation patrick-barnes
- Patrick Carmody App Charity Future Technologies Website patrick-carmody
- Patrick Larkin Cultural Music Painting patrick-larkin
- Paul Calnan 3D Character Design Design Thinking Film Sculpture Set Design Television paul-calnan
- Paul Doyle App Education Music paul-doyle
- Paul Gleeson Film paul-gleeson
- Peter Greene Cultural Print Making peter-greene
- Piyushi Dubey piyushi-dubey
- Rachel Doyle Crime Cultural Diversity Fashion History Music Performance Politics Social Justice rachel-doyle
- Rachel Lyons Design for Change Design Thinking Digital Design Environment Equality Ethics Fashion Social Justice User Experience Website rachel-lyons
- Rachel Mc Cabe Education Psychology rachel-mc-cabe
- Rebecca Lewis User Experience rebecca-lewis
- Rebecca Montague Psychology Science rebecca-montague
- Rebecca Osser Film rebecca-osser
- Reuben Harvey reuben-harvey
- Rían Kelleher App Design for Change Design Thinking Digital Design Education Environment User Experience rian-kelleher
- Roisin Malone Character Design roisin-malone
- Róisín Sinai Kelly roisin-kelly
- Ron Malecka ron-malecka
- Ross Malo ross-maloney
- Roxanne O'Brien Character Design Cultural Digital Design Drawing Family Film Illustration roxanne-o-brien
- Ruairi Barrett 3D Character Design Drawing Film Set Design ruairi-barrett
- Ruby Valdez App Cultural Design for Change Design Thinking Digital Design User Experience ruby-valdez
- Ryan Golden 3D Game Design ryan-golden
- Sam Bonney Music Space Exploration sam-bonney
- Sam Mc Mahon sam-mc-mahon
- Sam Nolan Logan Music sam-nolan-logan
- Sam O Neill Film sam-o-neill
- Sam Ardiff Branding Covid-19 Data Visualisation Installation samuel-ardiff
- Saoirse McGarry Film Music Performance saoirse-mc-garry
- Sorche Ní Ríain Drawing Environment Illustration Installation Painting Print Making Sculpture Wildlife sarah-berry
- Sarah Byrne Character Design Performance Sculpture sarah-byrne
- Sarah Hoffman 3D Design for Change Design Thinking Diversity Exhibition Design History Illustration Research Sculpture sarah-hoffman
- Sarah Partington sarah-partington
- Sarah Singa Education Healthcare Psychology sarah-singa
- Scott Li History scott-li
- Seán Óg Durack Monks App Future Technologies Music Website sean-durack-monks
- Sean Hannon Environment Film Wildlife sean-hannon
- Seán Kelly sean-kelly
- Sean Magill sean-magill
- Sean Ó' Síocháin Music Psychology sean-o-siochain
- Shane Smyth AI Data Visualisation Digital Design Performance Product Design Research User Experience Website shane-smyth
- Shona Doyle Cultural Energy Environment Sculpture Wildlife shona-doyle
- Simon Love 3D Film simon-love
- Sinead Casey sinead-casey
- Sinéad Gillain Equality Performance Politics sinead-gillain
- Siyuan Xu Character Design Film Illustration siyuan-xu
- Sophie Kathryn Covid-19 Data Visualisation Ethics Psychology Research Science sophie-kathryn
- Sophie Krywonis Environment Psychology sophie-krywonis
- Sophie O'Connor 3D Character Design Sculpture sophie-oconnor
- Sophie Smith Psychology sophie-smith
- Sorcha Fitzgerald Branding Cultural Design for Change Design Thinking Exhibition Design Motion Graphics User Experience sorcha-fitzgerald
- Stephen McCann Branding Business Education Entrepreneurship Radio Research stephen-mc-cann
- Sthiti Padhy Film Performance sthiti-padhy
- Susan James Branding Charity Crime Design Thinking Environment Fashion Film Protest Social Justice susan-james
- Szilard Ovari Design Thinking Engineering Future Technologies Music Product Design Research Science User Experience szilard-ovari
- Tadhg McDonogh Cunningham Film tadhg-mc-donogh-cunningham
- Tara Gavigan Character Design Digital Design Drawing Film tara-gavigan
- Tommy Kenny Book Music thomas-kenny
- Thomas Kerr App Music Research thomas-kerr
- Thomas Purdy Film thomas-purdy
- Tim Beary Data Visualisation Sports + Fitness tim-beary
- Tyrell McBride Film tyrell-mc-bride
- Val Myles Character Design val-myles
- Vanessa Zelek Painting wanessa-zelek
- Weronika Jakubowska Character Design Film Sculpture Television weronika-jakubowska
- Liam O william-olohan
- Wolf Chung wolf-chung
- Zerica Griffin Character Design zerica-griffin
- Zoë Barron 3D Character Design Film Painting Sculpture zoe-barron
- 3D Design Modelmaking + Digital Art
- Animation
- Applied Psychology
- Art
- Character MakeUp Design
- Costume Design
- Creative Computing
- Creative Media Technologies
- Creative Music Production
- Design for Change
- Film + Television Production
- New Media Studies
- Photography
- Production Design
- User Experience Design
- Visual Communication Design
- Home Homepage Index Overview


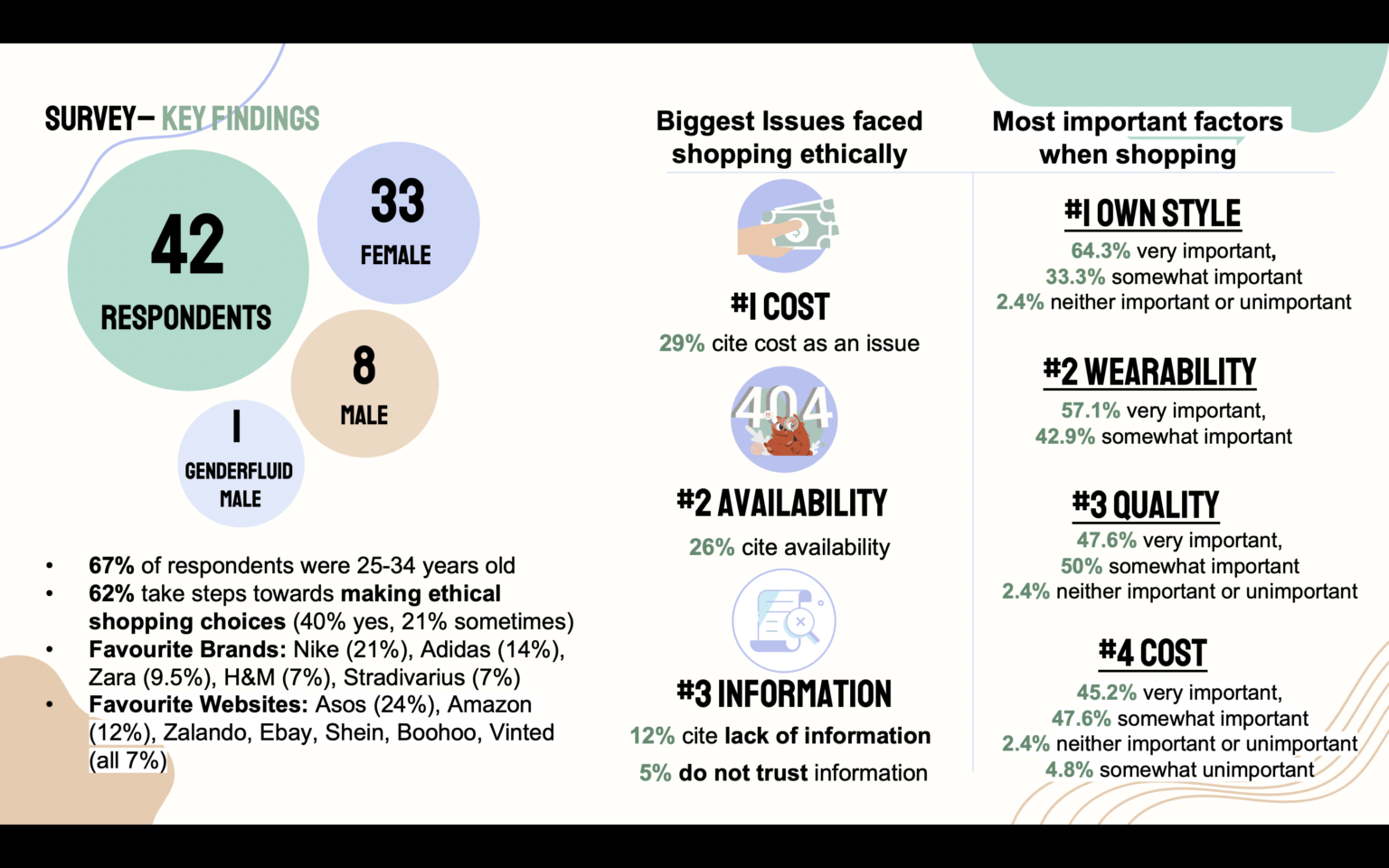
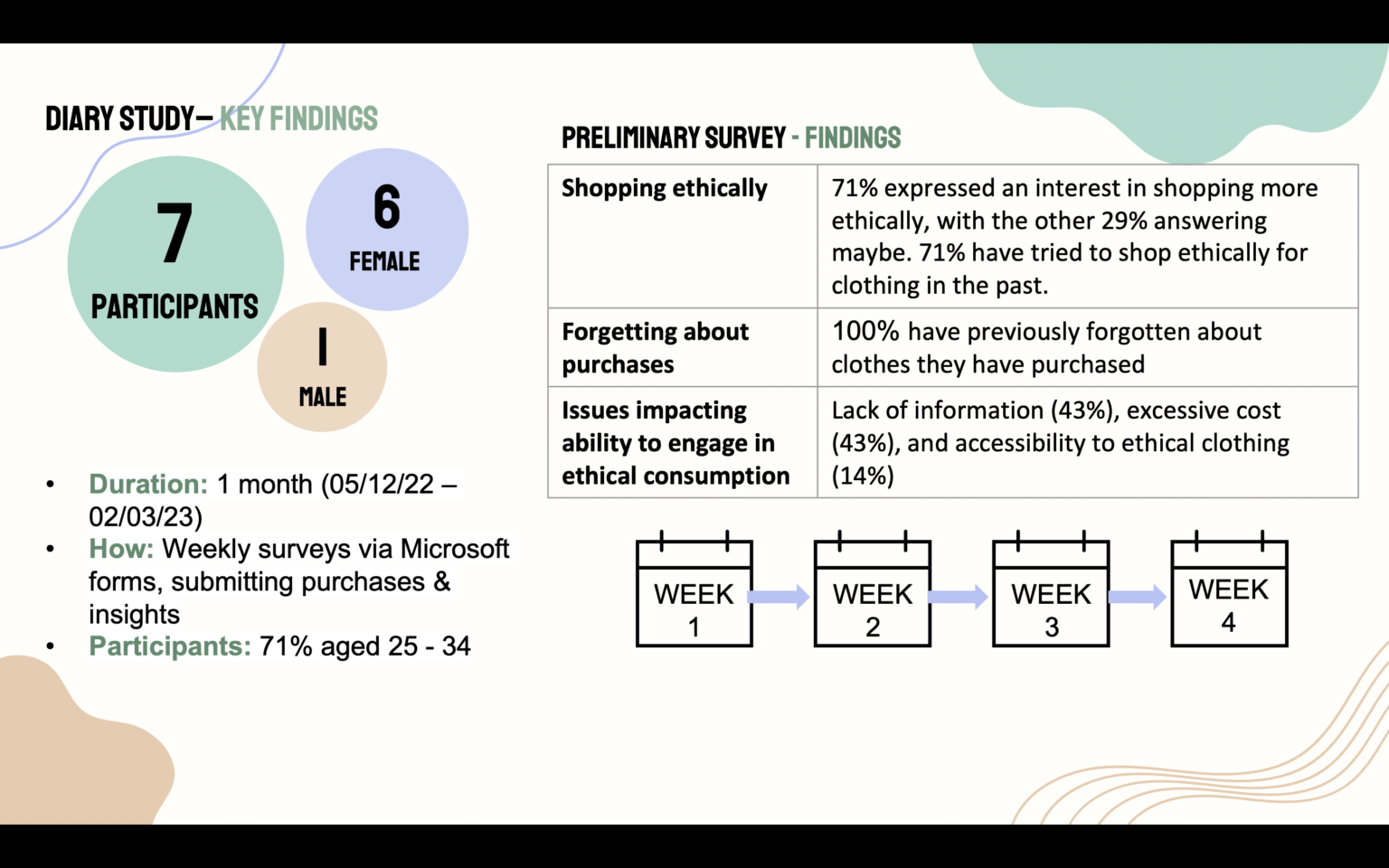
This study examines how digital nudges may be used to engage users moral identity, and how this may encourage users towards more ethical choices in an online environment.
Exploring the Impact of Moral Identity on online Purchasing Behaviours
As social media rises, so does consumers' awareness of the negative impacts of unethical, unsustainable production practices. With this rise in awareness has come an increase in consumers' desire to make more ethically and environmentally positive choices through their purchasing behaviors. Despite this interest in making more ethical choices studies have shown that there is a discrepancy, as users' desire to make positive shopping choices does not necessarily translate when examining their actual purchasing behaviours. Studies propose several factors may be impacting consumers' behaviors when trying to shop ethically, but the key factors which will be explored in this study will be the impact of moral identity on individuals shopping choices in an ethical fashion environment, and the role misinformation plays on impacting the choices individuals make. These concepts will be examined through a UX design lens by exploring how digital nudges may be used to encourage and facilitate more ethical shopping practices.